October 9, 2024
Introduction
The manufacturing industry is facing a significant transformation driven by the entry of new generations into the workforce and the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. These innovations are redefining production processes and business models, creating new growth opportunities but also significant challenges for the sector.
Intergenerational Challenges in Manufacturing
The Italian manufacturing sector is facing a significant challenge related to the coexistence of different generations in the workplace. This generational diversity, which mainly includes Baby Boomers, Generation X, Millennials, and Generation Z, brings a series of unique challenges and opportunities for companies in the sector.
One of the main challenges is the difference in expectations and approaches to work among different generations. Younger workers, particularly Millennials and Generation Z, tend to seek a greater work-life balance, flexibility in working hours, and opportunities for rapid growth. This contrasts with the more traditional approach of previous generations, who often value stability and long-term company loyalty.
Retention of young talent has become a critical challenge for the manufacturing sector. An alarming statistic reveals that the turnover rate for Generation Z and Millennials in the manufacturing sector reaches 51% in the first six months of employment (1). This phenomenon is particularly concerning considering that today, more than 30% of workers in the sector are over 50 years old, and it is predicted that this age group could become prevalent within ten years (2).
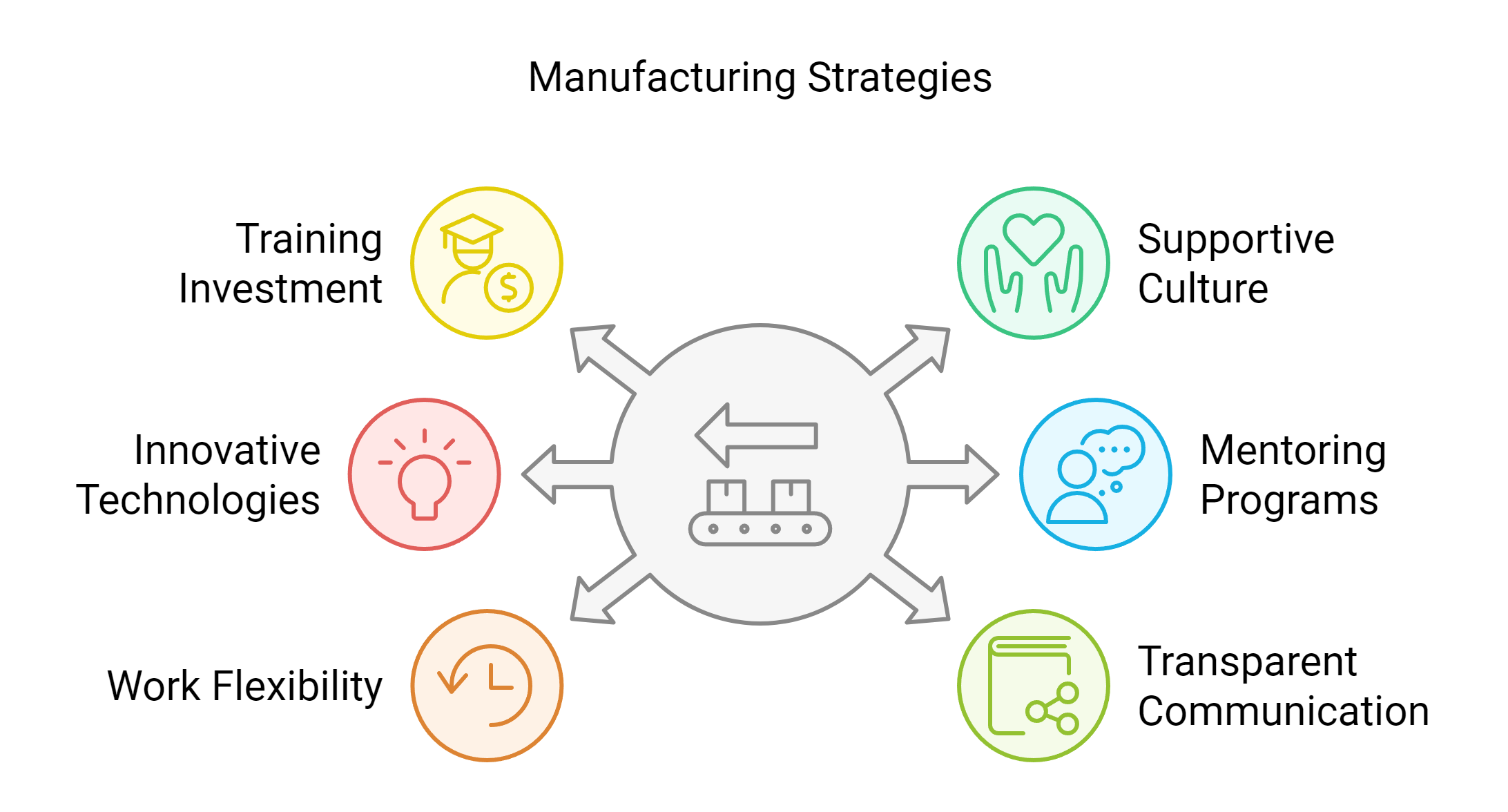
To address these challenges, Italian manufacturing companies are adopting various strategies:
- Investment in training and development
- Promotion of a supportive culture
- Adoption of innovative technologies
- Implementation of mentoring and reverse mentoring programs
- Work flexibility
- Open and transparent communication
The adoption of these strategies not only helps manage intergenerational challenges but can also bring significant benefits to manufacturing companies. Generational diversity, if managed effectively, can become a source of innovation and creativity, combining the experience of older workers with the new perspectives and digital skills of younger ones.
However, it is important to recognize that managing generational diversity requires a flexible and personalized approach. There is no one-size-fits-all solution, and strategies must be adapted to the specific needs and organizational cultures of each manufacturing company.
Digital Skills and Automation
The Italian manufacturing sector is undergoing a profound transformation driven by automation and digitalization, requiring a rapid adaptation of the workforce’s skills. This technological evolution is creating a growing demand for professionals with advanced digital skills, capable of managing and optimizing automated production processes.
The most sought-after digital skills in the manufacturing sector include:
– Programming and management of robotic systems and cobots (collaborative robots)
– Data analysis and data science for production process optimization
– Cybersecurity skills to protect interconnected systems
– Knowledge of IoT (Internet of Things) technologies for sensor and connected device management
– Proficiency in CAD/CAM software for computer-aided design and production
– Skills in augmented and virtual reality for maintenance and training
Automation is radically transforming traditional roles within factories. According to a study by the Department for European Affairs, by 2030, 80% of adults should possess at least basic digital skills (3). This change is creating new professional opportunities, such as specialized technicians in predictive maintenance, automation engineers, and industrial data analysts.
To address this challenge, many Italian manufacturing companies are investing in training and professional development of their employees. Upskilling and reskilling programs have become essential to bridge the skills gap and prepare the existing workforce for new technologies. At the same time, collaborations between industry and educational institutions are increasing, with the aim of aligning training paths with sector needs.
While automation requires new skills, it also offers opportunities to improve workplace safety and reduce physical workload. Cobots, for example, can take on repetitive and potentially dangerous tasks, allowing human operators to focus on higher value-added activities that require creativity and problem-solving.
However, the implementation of automation must be managed carefully to avoid technological unemployment. Italian manufacturing companies are adopting approaches that aim to integrate automation as a support to human work, rather than as a substitute. This “human-centric” strategy aims to create a work environment where humans and machines collaborate synergistically, leveraging the strengths of both.
Role of Generative AI
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) is emerging as a revolutionary technology in the Italian manufacturing sector, offering new opportunities to increase efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. This advanced technology is based on deep learning models capable of generating new content, analyzing large amounts of data, and providing valuable insights for decision-making.
In the context of the manufacturing industry, GenAI finds application in several key areas:
- Production optimization
- Predictive maintenance
- New product development
- Supply chain management
- Quality control
- Virtual assistance and training
The implementation of GenAI in the Italian manufacturing sector also presents significant challenges. Companies need to invest in adequate technological infrastructure, train staff in new digital skills, and address issues related to data security and privacy.
Despite these challenges, the adoption of generative AI offers significant competitive advantages. Manufacturing companies that successfully integrate this technology can expect increased productivity, reduced operating costs, and greater innovation capacity.
To maximize the benefits of GenAI, Italian manufacturing companies must adopt a strategic approach, identifying the areas where the technology can offer the maximum value and investing in continuous staff training. Collaboration between different generations of workers, combining the experience of veterans with the digital skills of younger ones, will be crucial to fully exploit the potential of generative AI and drive the digital transformation of the Italian manufacturing sector.
Implementation of Digital Twins
The implementation of digital twins is revolutionizing the Italian manufacturing sector, offering new opportunities to optimize production processes and improve operational efficiency. A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical asset, continuously updated and synchronized in real-time. This technology allows companies to monitor, analyze, and optimize their operations in previously impossible ways.
In the context of the Italian manufacturing industry, digital twins find application in several key areas:
– Product design and development
– Predictive maintenance
– Process optimization
– Staff training
The adoption of digital twins requires an advanced technological infrastructure, including IoT sensors, data analysis systems, and cloud platforms for information processing and visualization. Italian manufacturing companies are investing in these technologies to remain competitive in the global landscape of Industry 4.0.
However, the implementation of digital twins also presents significant challenges. Managing and analyzing large amounts of data require specialized skills and investments in IT infrastructure. Moreover, integrating digital twins with existing legacy systems can be complex and costly.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits are significant. Companies that have successfully implemented digital twins have recorded significant improvements in terms of operational efficiency, cost reduction, and increased product quality. This technology is becoming increasingly crucial for Italian manufacturing companies aiming to maintain their competitiveness in a rapidly evolving global market.
Real-Time Data Analysis
Real-time data analysis is revolutionizing the Italian manufacturing sector, allowing companies to optimize production processes and make faster, more informed decisions. This technology enables the collection, processing, and analysis of enormous amounts of data from machinery, sensors, and production systems instantaneously, providing valuable information to improve operational efficiency.
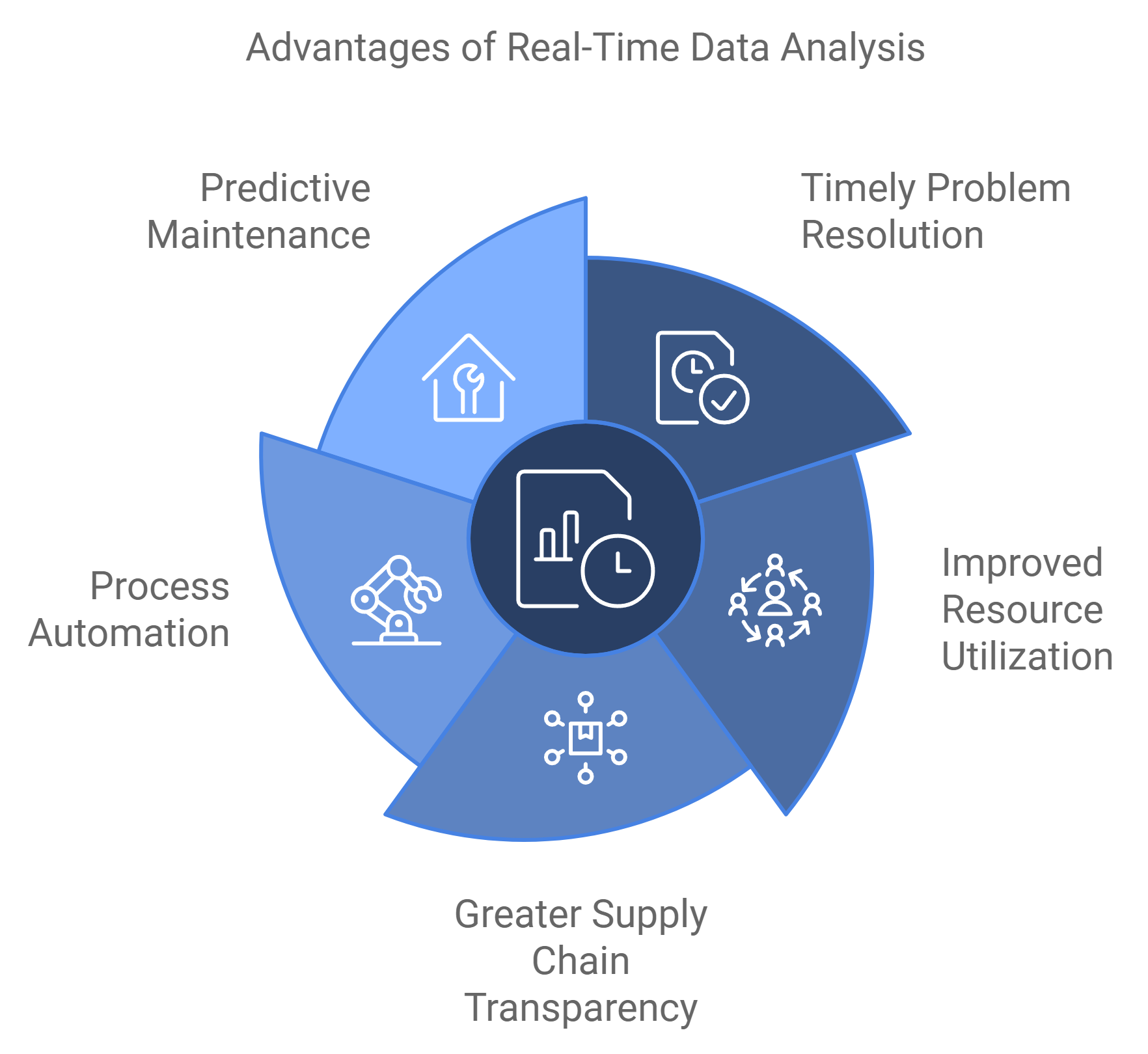
The main advantages of real-time data analysis include:
- Timely identification and resolution of problems
- Improved resource utilization
- Greater supply chain transparency
- Process automation
- Predictive maintenance
The implementation of advanced technologies such as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Edge Computing, and artificial intelligence has made large-scale real-time data analysis possible. These technologies allow for the processing of large volumes of data directly on-site, reducing latency and enabling near-instantaneous responses to changes in production conditions.
However, the implementation of real-time data analysis also presents challenges. Companies need to invest in adequate technological infrastructure and train staff to interpret and act on data effectively. Additionally, managing and protecting large amounts of sensitive data require robust cybersecurity measures.
Despite these challenges, the adoption of real-time data analysis is becoming increasingly crucial for Italian manufacturing companies that want to remain competitive in the global market. Companies that manage to effectively leverage this technology can expect significant improvements in terms of operational efficiency, product quality, and responsiveness to market needs.
Continuous Training and Adaptability
Continuous training and adaptability have become essential components for the success of the Italian manufacturing industry in the era of Industry 4.0. With the rapid evolution of technologies and production processes, companies are increasingly investing in employee training to maintain competitiveness and innovation.
In 2021, 57% of Italian companies invested in training programs for their employees, a significant increase compared to 49% recorded in 2020 (4). This increase was driven by the need to adapt to new work models, such as remote work and the adoption of digital technologies, which emerged during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Continuous training in the manufacturing sector focuses on several key areas:
- Technical skills
- Soft skills
- Safety and compliance
- Sustainability
Manufacturing companies are adopting innovative approaches to training, including:
– E-learning platforms
– Virtual and augmented reality
– Mentoring programs
Investment in continuous training produces tangible results. According to an Assolombarda report from 2023, companies that invested in continuous training programs recorded a 15% increase in productivity compared to those that did not undertake such initiatives (5). Moreover, these companies saw a 10% reduction in staff turnover, highlighting how training can improve employee satisfaction and retention.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which form the heart of the Italian economy, are increasingly recognizing the importance of continuous training. A Confartigianato survey in 2022 revealed that 65% of SMEs increased their training budget compared to the previous year (6).
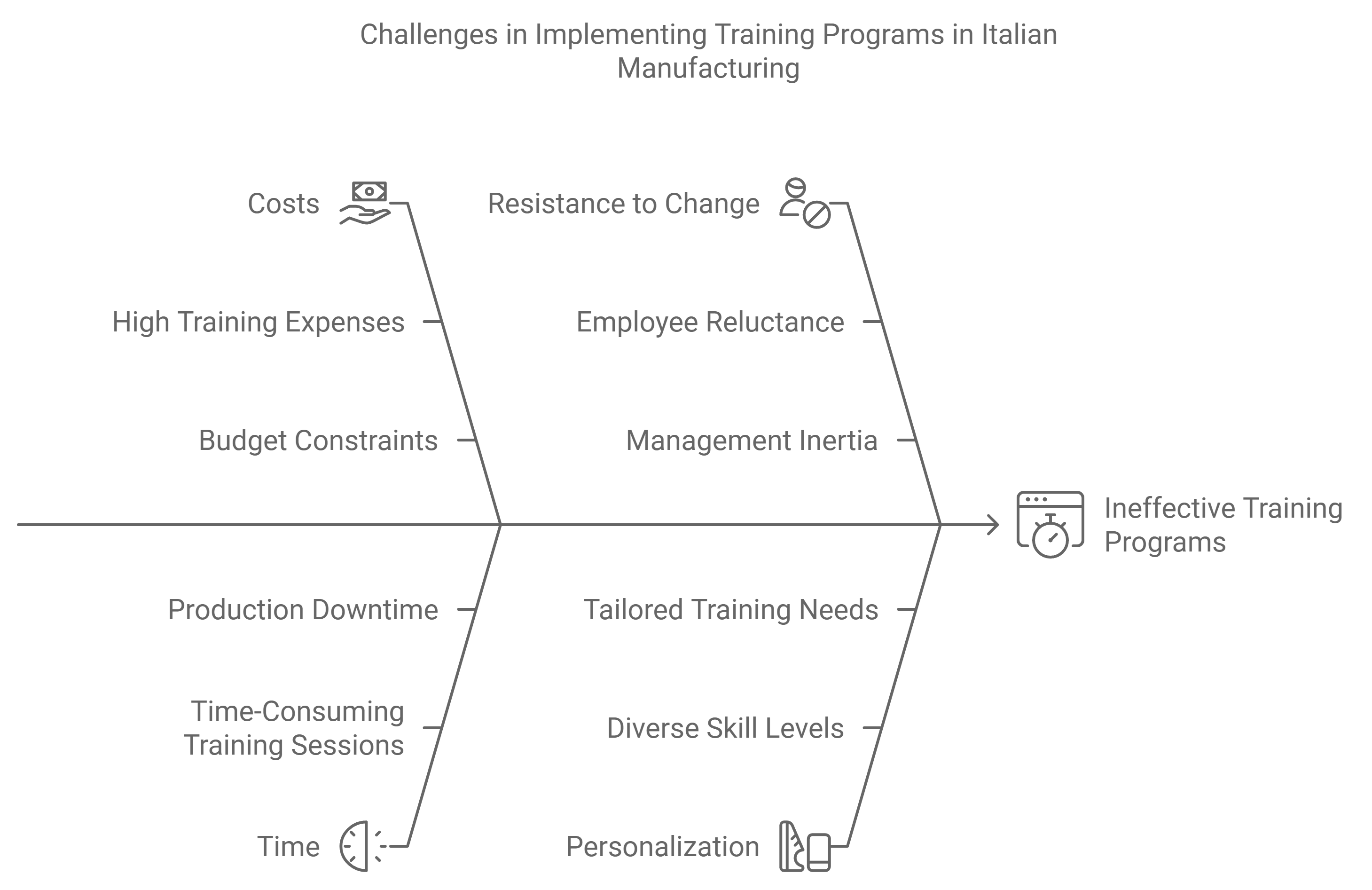
However, Italian manufacturing companies face significant challenges in implementing effective training programs:
- Costs
- Time
- Resistance to change
- Personalization
To overcome these challenges, many companies are collaborating with universities and vocational training institutes. Online universities play an important role in this transition, offering flexible and personalized programs that adapt to the needs of the manufacturing sector.
Conclusions: Future Challenges and Opportunities
The Italian manufacturing industry is facing an epochal transformation, driven by technological innovation and the entry of new generations into the workforce. This evolution presents both significant challenges and extraordinary opportunities for the sector.
The adoption of advanced technologies such as generative Artificial Intelligence, digital twins, and real-time data analysis is redefining production processes, improving efficiency, and opening new possibilities for innovation. However, these technologies require constant updating of workforce skills, making continuous training a crucial element for companies’ competitiveness.
The generational gap represents a significant challenge, with a high turnover rate among young workers. This phenomenon highlights the need for targeted strategies to attract and retain talent, creating work environments that meet the expectations of new generations without neglecting the experience of older workers.
Digitalization and automation are radically transforming traditional roles, with a prediction that by 2030, most jobs in the Italian manufacturing sector will require advanced digital skills. This change requires a significant commitment to upskilling and reskilling the existing workforce, as well as close collaboration between industry and educational institutions to align training paths with sector needs.
In conclusion, the future of the Italian manufacturing industry will depend on companies’ ability to embrace technological innovation, invest in continuous training, and create inclusive work environments that value the skills of all generations. The challenges are considerable, but the opportunities for growth and innovation are equally significant. Companies that manage to successfully navigate this transition will be well-positioned to thrive in the era of Industry 4.0 and beyond.
Sources:
(1) https://antsolutions.eu/it/blog/perche-i-giovani-lavoratori-abbandonano-i-posti-di-lavoro-nel-settore-manifatturiero-unanalisi-approfondita-del-tasso-di-turnover-51/
(2) Invecchiamento della forza lavoro e pratiche di age-management nella cooperazione sociale del territorio di Bergamo – ISBN 978-88-31940-67-2
(3) https://www.affarieuropei.gov.it/it/comunicazione/notizie/anno-ue-competenze/
(4) https://www.econopoly.ilsole24ore.com/2024/06/28/formazione-continua-aziende-universita/
(5) https://www.econopoly.ilsole24ore.com/2024/06/28/formazione-continua-aziende-universita/
(6) https://www.econopoly.ilsole24ore.com/2024/06/28/formazione-continua-aziende-universita/